Contact or visit us to learn more about a neurological condition or pain and we will help. Our world renowned doctors are dedicated to providing you with the best service with the highest integrity.
Seattle Neuroscience Institute
- Home
- Conditions & Treatments
- Arteriovenous Malformation AVM
- Brain Aneurysm | Cerebral Aneurysm
- Carotid Artery Disease
- Cavernous Malformations
- Colloid Cyst
- Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
- Hemifacial Spasm
- Meningioma
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
- Moyamoya Disease
- Spinal Canal and Spinal Cord Tumors
- Transient Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment
- Research & Publications
- Practice Locations
- About
- Contact
Neurological Conditions
Arteriovenous Malformation AVM
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a tangled group of blood vessels with abnormal connections between arteries and veins. AVMs are rare — affecting less than 0.1 percent of Americans.
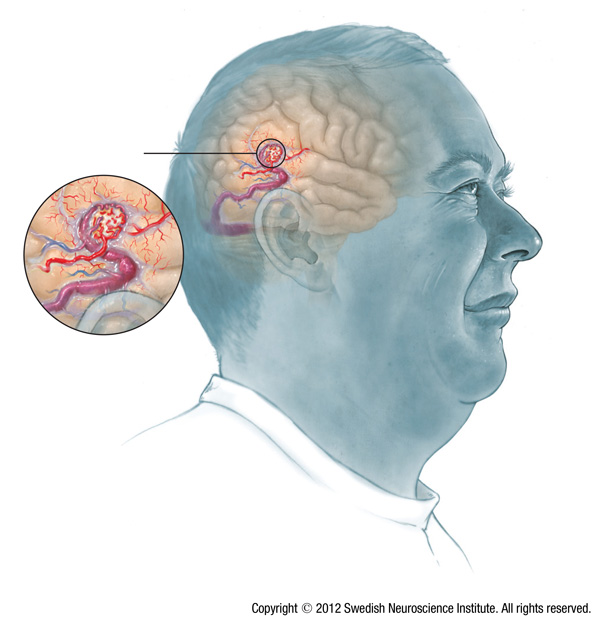
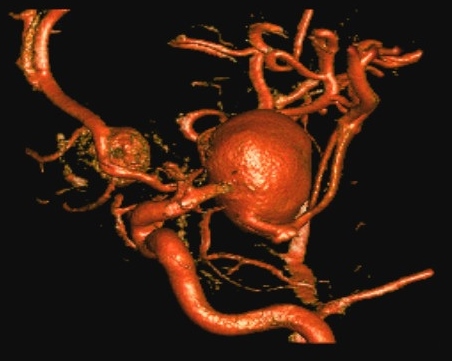
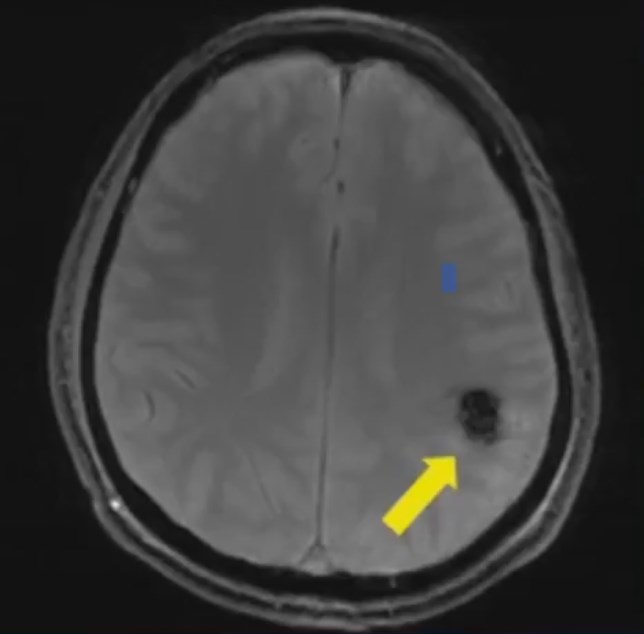
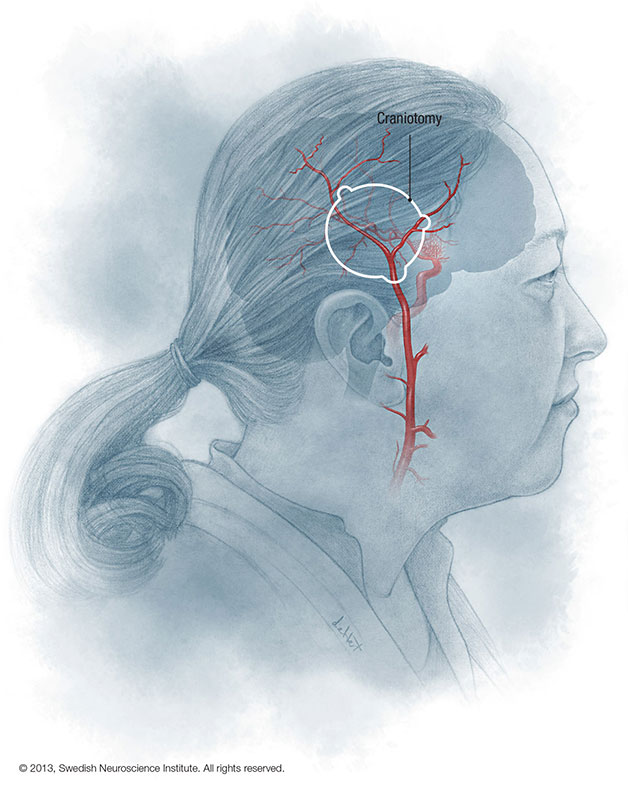
Brain Aneurysm / Cerebral Aneurysm
A brain aneurysm (also called a cerebral aneurysm) is a blister-like bulge in a weak part of a blood vessel in your brain. Although many people think a brain aneurysm or cerebral aneurysm means sudden, unexpected death, this condition can be both survivable and treatable in most cases.
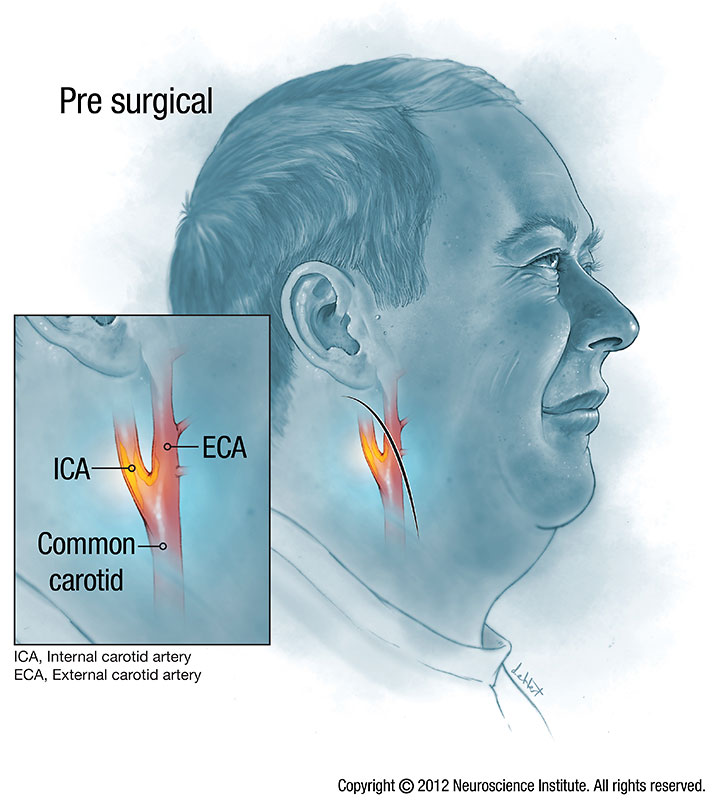
Carotid Artery Disease
The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain. Carotid artery disease, also known as carotid atherosclerosis, occurs when there is a buildup of plaque in these arteries in the neck in most cases.
Cavernous Malformations
Cavernous malformations are clusters of abnormal, tiny blood vessels, and larger, stretched-out, thin-walled blood vessels filled with blood in the brain. These blood vessel malformations can also occur in the spinal cord, the covering of the brain (dura), or the nerves of the skull.
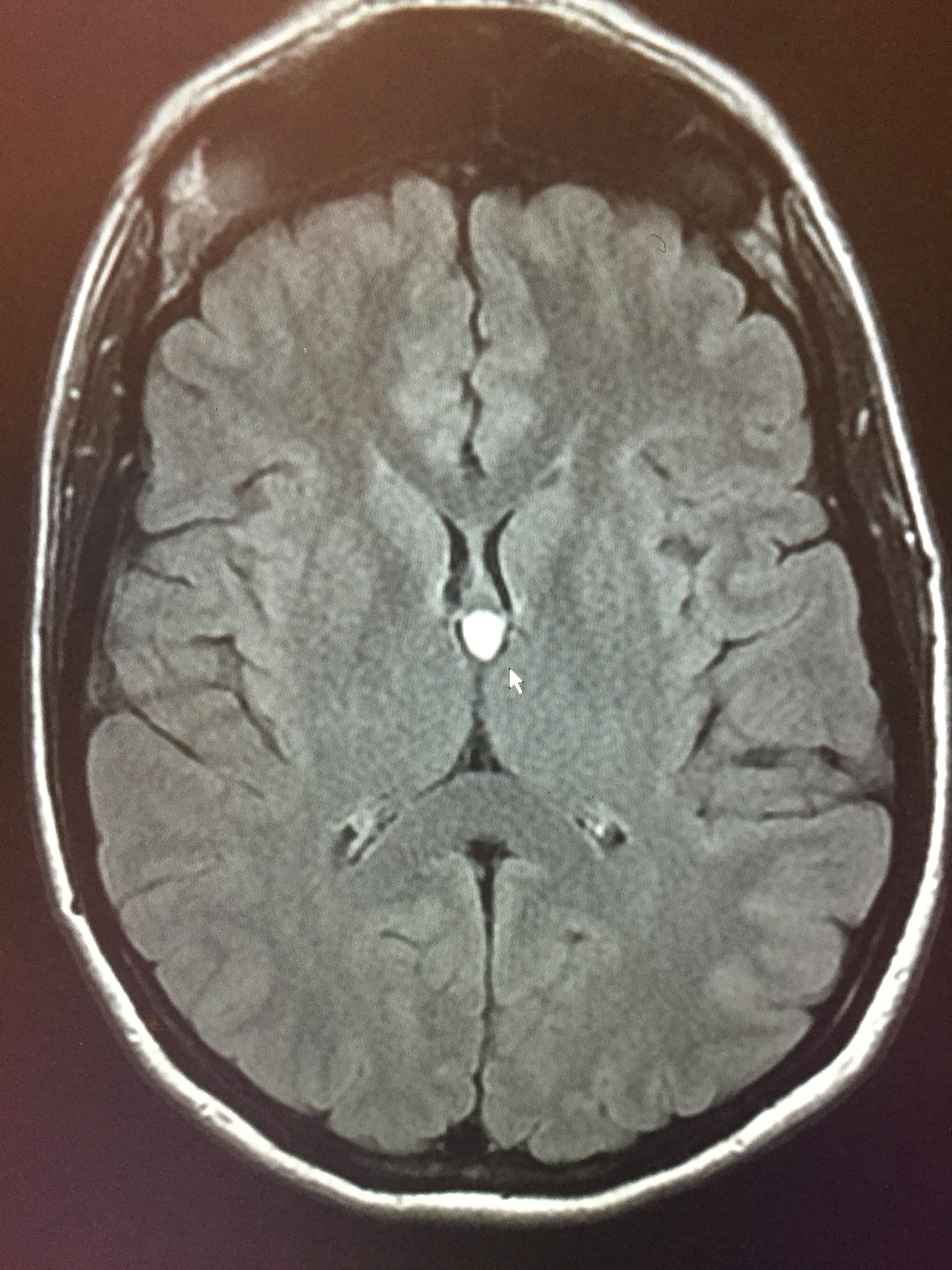
Colloid Cyst
A colloid cyst is a cyst containing gelatinous material in the brain. It is almost always found just posterior to the foramen of Monro in the anterior aspect of the third ventricle, originating from the roof of the ventricle.
Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GN) is a rare pain syndrome that affects the glossopharyngeal nerve (the ninth cranial nerve that lies deep within the neck) and causes sharp, stabbing pulses of pain in the back of the throat and tongue, the tonsils, and the middle ear.
Hemifacial Spasm
Hemifacial spasm is a neuromuscular disorder that causes frequent involuntary contractions to occur in the muscles on one side of the face.
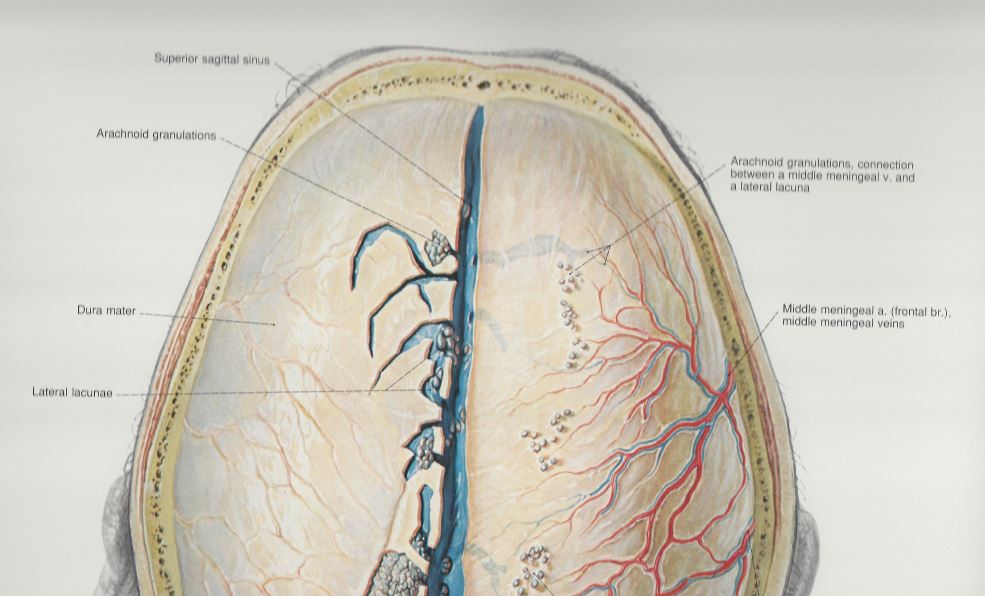
Meningioma
A meningioma is a tumor that grows from the dura which is part of the meninges, the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are noncancerous (benign), though rarely a meningioma may be cancerous (malignant).
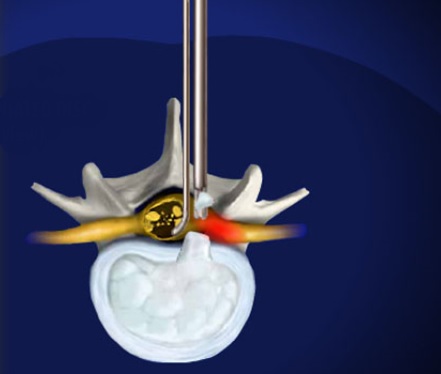
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Cervical and lumbar radiculopathy means nerve root irritation coming from the cervical spine or neck or the lumbar spine or low back. The most common causes of these conditions are disc disease or bone spurs which can irritate the nerves.
Moyamoya
Moyamoya disease is a progressive disorder of the cerebral vessels, characterized by narrowing of the intracranial vessels as they emerge from the base of the skull. Moyamoya means ‘puff of smoke’ in Japanese, and refers to the look of the tiny vessels appearing on cerebral angiography in patients with this condition. Moyamoya disease is progressive and the underlying cause is unknown.
Spinal Canal and Spinal Cord Tumors
Spinal tumors are broadly classified into tumors which are located in or arise from the vertebral and bony elements of the spine, and those which occur in the spinal canal. They can also be referred to according to the regions of the spine in which they are located which are termed cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. Spinal canal tumors can arise from the tissues covering the spinal cord and are called either exdradural or intradural depending on whether they are on the outside or the inside of the dural membrane which contains the spinal fluid, nerve roots and spinal cord.
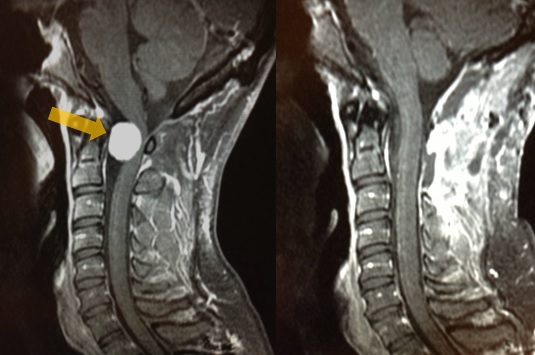
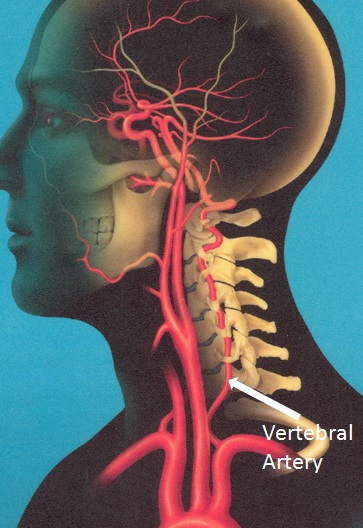
Transient Vertebrobasilar Insufficiency
Transient vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI) caused by head turning, also known as head turning syncope, is increasingly being recognized as a potentially incapacitating and debilitating condition. It refers to a reduction in blood flow to the posterior part of the brain and posterior cerebral circulation caused by turning the head and temporarily blocking blood flow through the veretebral artery in the neck.
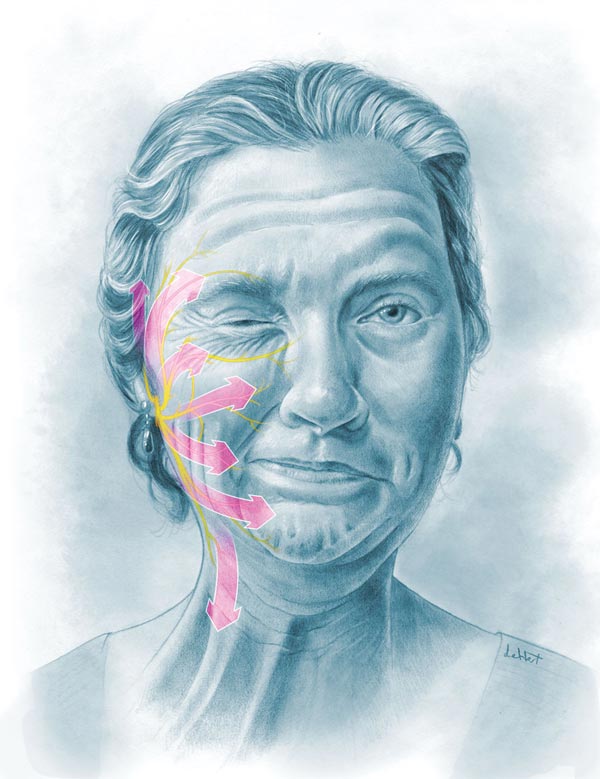
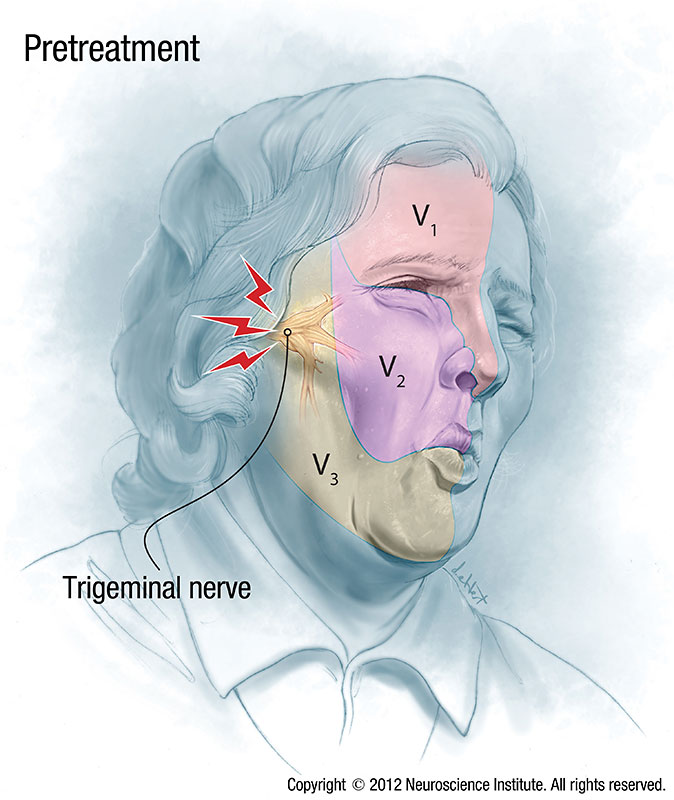
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia, also called tic doloureux, is a condition characterized by episodes of intense facial pain that lasts from a few seconds to several minutes or hours. The pain occurs in areas of the face where the trigeminal nerve supplies normal sensation: cheek, jaw, teeth, gums and lips, and sometimes the eye or forehead. This condition causes sudden, sharp and very severe pain, usually only on one side of the face.